Key takeways
- RPA helps businesses accelerate their digital transformation efforts and boost their Return on Investment (ROI) from their employees.
- Drivers of RPA evolution include automation, workflow management, and AI.
- AI and RPA work in tandem when integrated to create a more robust platform for hyper-automation. You can automate any front or back-office business process and combine human-bot teams to coordinate work.
- While traditional RPA bots automate processes based on structured data, intelligent automation can also work on unstructured data like scanned documents, emails, voice recordings, and more.
- In the future, we are likely to see more widespread adoption of attended automation that enhances the functionality of RPA bots.
One of the pathbreaking technologies that has taken the business world by storm is Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Also known as software robotics, RPA uses automation technology to mimic human back-office tasks, such as: Combining API and user interface (UI) interactions to integrate and perform repetitive tasks across enterprise and productivity applications. RPA bots provide scripts that emulate human processes and automate multiple activities and transactions independently without human intervention.
With the help of rule-based software, RPA automation performs different business processes at scale. This frees up human resources who can focus on complex, skill-based tasks. RPA helps businesses accelerate their digital transformation efforts and boost their Return on Investment (ROI) from their employees. According to one report, companies have reduced operating costs by 30% through hyper-automation technology and operational redesign. Surveys claim that RPA software’s revenue will generate 1,888.1 million between 2023 and 2028. (Source: www.gartner.com)
Forefathers of RPA
RPA combines multiple technologies into one toolkit for various automation purposes. “RPA” was coined in the early 2000s, but the first developments began in the 1990s. One of the prime movers for the innovations that ultimately led to the development of RPA is Machine Learning (ML). It enables computers to perform important tasks such as translations and text summaries.
Screen-scraping technology is considered an important step in creating RPA. This technology extracts data from the web, programs, and documents, further viewed in another application. Although screen scraping had many advantages over manual methods, it was also somewhat limited. The limitations and lack of availability of source code, programmers, and documentation made it difficult for the average business user to understand it.
Drivers contributing to the RPA evolution
Drivers that have contributed to the RPA evolution include:
1. Automation
Workflow automation is a process involving a series of automated actions that help reduce human work. These actions should be iterative so that the steps are predictable. Such actions can be automated using automated management tools. Workflow automation uses business rules to determine when one step is complete, and the next step is ready to begin execution. The automotive and electronics sectors will drive a significant increase in global shipments of industrial robots, which accounts for about 23% and 31% of new installations in 2020, respectively. (Source: www.statista.com)
Automation in its original form has existed since the Industrial Revolution. It briefly describes the process that takes place without manual input. In the 1990s automation was introduced into computer processing. In particular, the rise of graphical user interfaces has created a need for automation at every level.
When someone clicks the button, an automated process starts in the background, taking you to the next step and registering and tracking the button click. With the evolution of digital tasks from simple button clicks to complex macros, RPA evolved into more complex tasks as well.
Data shows that 28% of those opting for RPA are also investing in cognitive automation. (Source: www2.deloitte.com)
2. Workflow Management
In its simplest form, workflows streamline everyday processes and activities. They are essential for any business looking to build complex processes, from production and internal task management to lead and customer follow-up. Workflow management is the “P” in RPA. It is a process waiting to be automated. Over the years, the third factor of RPA has moved more and more toward that position.
3. Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the ability of computer machines or robots to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. AI programming depends on three techniques: Learning, reasoning, and self-correction. Artificial intelligence applications are endless and can be applied in various fields and industries. Big data is projected to reach 163 trillion gigabytes by 2025. This big data growth is driving improvements in AI algorithms. (Source: www.statista.com)
The concept of artificial intelligence was introduced as early as the 1950s. Today, using computers to perform tasks beyond their strictly prescribed boundaries is vital.
It is the third component, the “A” in RPA. Artificial intelligence enables automated workflows to go beyond simple tasks by automating and improving complex processes over time. Instead of focusing automation on rule-based processes that do not allow exceptions, the AI’s self-improving component can cover those exceptions and even create rules specifically for the exceptions it finds. The AI companies have successfully raised US $188 billion by 2021. (Source: https://www.statista.com/study/50485/in-depth-report-artificial-intelligence/ ). The market of RPA will grow to 8 billion USD by 2023. (Source: www.statista.com)
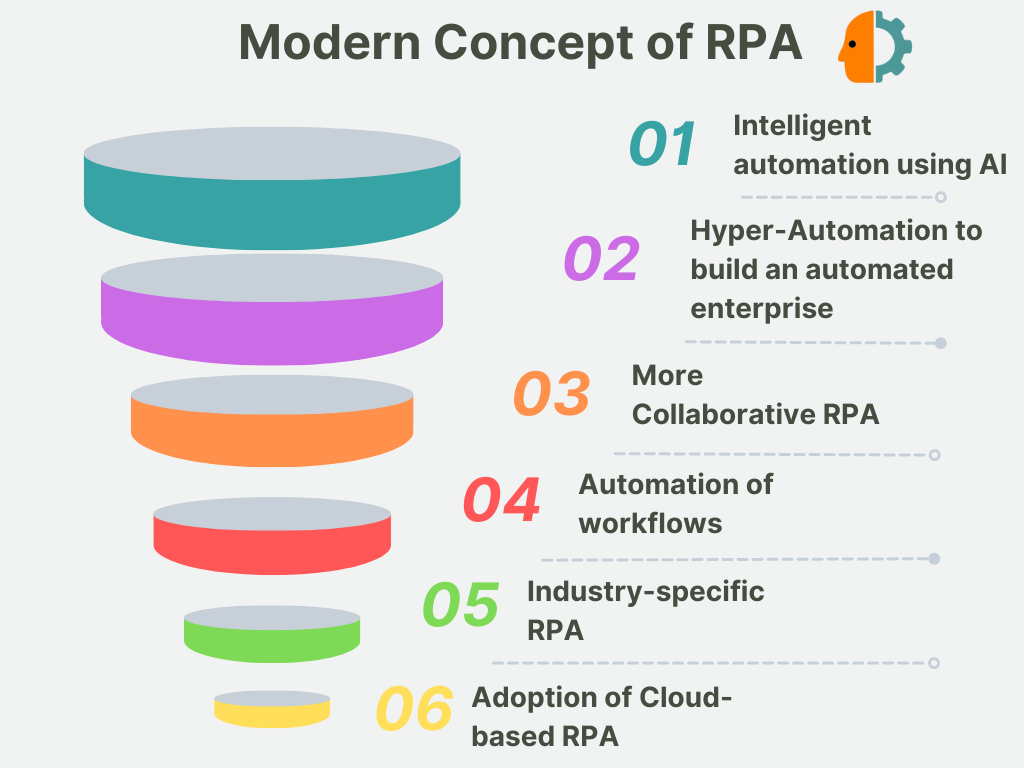
Modern RPA Concept
Key trends in modern concepts in RPA are:
1. Industry-specific RPA
Organizations in various industries, like healthcare, IT, finance, and manufacturing, include specific automation needs based on their day-to-day operations. For this reason, there is an increasing tendency for RPA vendors to develop out-of-the-box, industry-specific solutions tailored to the needs of these companies based on their industry.
2. Widespread Adoption of Cloud-based RPA
The move to a fully cloud-based RPA solution is one of the notable RPA trends. Most vendors today offer on-premises solutions to build robots that automate routine and manual tasks. As more and more companies store their data in the cloud, RPA solutions are also available to enable rapid system integration and data access.
3. More Collaborative RPA
Collaborative robotic process automation includes smoothly integrating RPA with other intelligent automation technologies, such as BPM and BPA tools. This approach helps companies fully automate most processes, regardless of their level of complexity. The ability to automate processes between the two most advanced technologies ever created helps streamline processes faster, leading to lower costs and increased productivity.
Impact of AI on RPA: Intelligent automation or hyper-automation
AI and RPA work in tandem when they are integrated to create a more robust platform for hyper-automation. You can automate any front or back-office business process and combine human bot teams to coordinate work.
Here are some reasons to use RPA and AI in one package:
- Improve employee productivity.
- Free your employees from painful, monotonous, repetitive tasks.
- Eliminate human error in the workplace and ensure accurate results.
- Save costs by improving the efficacy of data management.
- Customized dashboards and reporting support give you complete visibility into your processes.
A survey shows that 38% of marketing leaders and 46% of IT managers depend on these technologies daily. (Source: www.redicalcompliance.com)
4. Automation of workflows with RPA and AI
AI, in particular, can significantly impact how RPA deploys and works. While many tasks automated by RPA may seem simple, software program tasks can be complex. AI can handle increasingly complex tasks as it becomes more robust and learns to interact in dynamic environments.
Automation software is usually limited to rule-based processes where deviations are unexpected. It is severely limited to what could be automated. However, when RPA software gets infused with AI, it can handle exceptions. It will allow you to automate many more tedious processes.
Future of RPA
A peek into the future of RPA reveals that there is a lot more in store! In the future, we are likely to see more widespread adoption of attended automation that enhances the functionality of RPA bots. An attended bot is essentially software that exists on the desktop and automates rule-based tasks and guides employees to enhance outcomes.
We are moving towards an era of smarter automation where attended automation will work with AI and RPA tools. A blend of these technologies is known by different names like intelligent automation, intelligent process automation, or cognitive RPA. Intelligent automation increases the scope of traditional RPA by facilitating the automation of less rule-based and more complex tasks. While traditional RPA bots automate processes based on structured data, intelligent automation can also work on unstructured data like scanned documents, emails, voice recordings, and more.
Cognitive automation will help businesses automate both front-end and back-end office tasks seamlessly and enhance customer experience, which is the ultimate goal of any business.
If you are considering RPA for your business:
- Make sure you meet your leadership team’s expectations before making any decisions.
- Discuss the risks of RPA implementation and what can happen if expectations are unrealistic.
- By setting realistic goals from the start, you can avoid overspending while maintaining team morale.
Or, you can simply consult the professionals at Auxiliobits for custom automation solutions!
What we can do for you?
We work with you to understand your automation goals and recommend the best RPA tools to achieve them. Our professionals have an in-depth understanding of automation technologies and we help choose cost-effective automation solutions that integrate easily with their existing systems.
Call Us Now for the Best Automation Solutions!
Watch this space for our upcoming blogs on automation!




 April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024
