Key Takeaways
- Robotic Process Automation streamlines routine, rule-based financial processes such as journal entries, reconciliations, and disclosures, helping finance teams more efficiently meet SOX and IFRS standards.
- By eliminating human error and maintaining detailed logs of every action, RPA improves the accuracy of financial reports and strengthens audit trails, which are essential for SOX and IFRS compliance.
- RPA enforces internal controls automatically and supports segregation of duties by assigning different bots to different tasks, which is crucial for SOX compliance.
- RPA automates complex calculations and standardizes financial data across systems and geographies, ensuring consistent and compliant IFRS disclosures globally.
- Starting small with repetitive tasks, involving compliance teams early, and choosing the right tools can make RPA adoption smooth and effective, even for teams with limited experience.
In today’s fast-paced business world, finance teams are constantly pressured to comply with strict regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). These regulations ensure transparency, accuracy, and honesty in financial reporting. But staying compliant isn’t easy—it involves a lot of repetitive, manual work, tight deadlines, and zero tolerance for errors.
This is where robotic process automation comes into play.
RPA is changing the game by automating routine tasks, improving accuracy, and reducing the burden on finance professionals. This blog will explore how RPA supports compliance with SOX and IFRS and how finance teams can benefit from this technology.
Also read: AI-Powered Energy Optimization in Manufacturing Facilities: ROI Analysis.
What is RPA?
Before we dive into compliance, let’s understand robotic process automation (RPA). RPA is software that mimics human actions to complete repetitive tasks. These “robots” or “bots” can log into systems, enter data, copy and paste information, move files, generate reports, and much more, just like a human would.
The key difference is that bots:
- Work 24/7
- Don’t make errors (when programmed correctly)
- Work much faster than people.
This makes RPA a perfect solution for finance teams overloaded with tasks and facing strict compliance deadlines.
A Quick Overview of SOX and IFRS
Understanding financial regulations is crucial for businesses operating in today’s global economy. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are essential frameworks. Although they serve different purposes and are applied in other regions, both aim to improve financial transparency and trust.
What is SOX?
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) is a U.S. law passed in 2002. It was created in response to major corporate scandals involving Enron and WorldCom, which shook investor confidence and caused significant financial losses. The main goal of SOX is to protect investors by ensuring that companies report their financial information accurately and honestly.
SOX places strict requirements on public companies, especially on their finance teams. Some of the key responsibilities under SOX include:
- Accurate Financial Reporting: Companies must ensure that all financial data reported is truthful and complete.
- Strong Internal Controls: Businesses must implement procedures and systems that prevent errors or fraud.
- Audit Trails: Every transaction must be documented, making it easy to trace how and when it occurred.
- Timely Reporting: Companies must share financial reports on time, ensuring investors can always access the latest information.
Non-compliance with SOX can lead to heavy penalties, including fines and even prison time for executives.
What is IFRS?
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are global accounting rules developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). Unlike SOX, which is a U.S. law, IFRS is used by companies in over 140 countries, including the European Union, Australia, and Canada. The United States still uses its Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) system.
The goal of IFRS is to standardize financial reporting across countries, making it easier for investors and regulators to understand and compare companies worldwide. Key benefits include transparency, consistency, and fairness in financial statements.
To comply with IFRS, companies must:
- Perform complex calculations and disclosures, especially for assets, liabilities, and revenue.
- Apply accounting policies consistently across reporting periods.
- Provide detailed documentation and justification for financial decisions.
To sum up, SOX ensures companies in the U.S. report honestly, while IFRS creates a global language for financial reporting. Both frameworks are essential for building trust in financial markets.
How does RPA Support SOX Compliance?
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires companies to ensure their financial reporting is accurate, transparent, and secure. Finance teams must follow internal controls, maintain audit trails, and meet reporting deadlines while avoiding errors and fraud. This can be a heavy burden, especially with manual processes.
That’s where robotic process automation comes in. RPA uses software “bots” to perform repetitive tasks quickly and consistently. Let’s explore how RPA helps finance teams stay compliant with SOX.
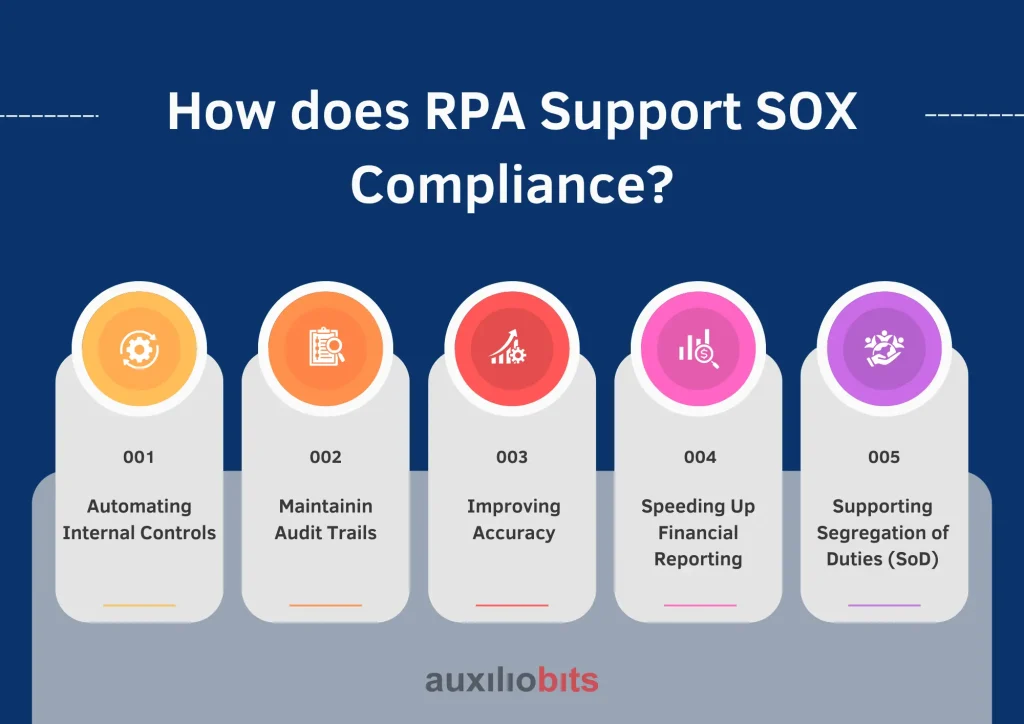
1. Automating Internal Controls
SOX requires companies to implement strong internal controls over financial reporting. These procedures ensure that economic data is appropriately handled. RPA bots can help by automatically performing these controls regularly.
For example:
- Bots can run daily checks on transactions to ensure they follow company policies.
- They can compare entries in the system with approval rules.
- The bot can flag the exception and alert a manager if something looks suspicious or incorrect.
Because bots follow instructions exactly, they apply these controls consistently, reducing the risk of human errors or fraudulent behavior.
2. Maintaining Audit Trails
SOX also requires companies to maintain clear audit trails—records that show exactly who did what and when. This is where RPA shines. Every time a bot runs a task, it creates a detailed log of its actions.
These logs include:
- Which data was accessed
- What operations were performed
- What changes were made
This makes it much easier for auditors to trace actions and verify that processes work as intended. These digital records are also easier to store and search than paper-based or manual logs.
3. Improving Accuracy
Manual data entry can lead to mistakes, especially when dealing with complex financial reports or large datasets. Copy-paste errors, missed steps, and miscalculations can all create compliance risks.
RPA helps avoid this by automating tasks that follow clear rules. Bots perform processes the same way every time, with no variation or fatigue. This means:
- Fewer errors
- More accurate reports
- Less time fixing mistakes
As a result, companies are better protected against compliance violations and can present cleaner records during audits.
4. Speeding Up Financial Reporting
SOX requires companies to report financial results within tight deadlines. Gathering data from different systems and preparing reports can be time-consuming, especially with manual work.
RPA bots can:
- Pull data from multiple software systems
- Merge and organize the information.
- Format and send reports automatically
This reduces the time it takes to create reports and allows finance teams to focus more on reviewing the data and making decisions, not just collecting and organizing it.
5. Supporting Segregation of Duties (SoD)
SOX also emphasizes segregation of duties (SoD)—the idea that no one person should control all steps of a financial process. RPA can help enforce this by dividing tasks among different bots.
For example:
- One bot creates a payment
- A second bot reviews and approves it (based on pre-set rules)
- A third bot records the transaction and sends a notification.
This automated separation of duties reduces the chance of fraud and strengthens internal controls.
RPA is a powerful tool for helping companies meet SOX requirements. It increases accuracy, speeds up work, maintains strong records, and improves control. By reducing manual effort and risk, RPA allows finance teams to focus on what matters most—ensuring compliance and building stakeholder trust.
How RPA Helps with IFRS Compliance?
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are global accounting rules that help companies consistently, transparently, and fairly report financial information. Businesses in over 140 countries use these standards. However, complying with IFRS can be complex and time-consuming, especially when financial data comes from multiple systems or requires detailed calculations and disclosures.
Robotic Process Automation can make this process much easier. RPA uses software bots to quickly, accurately, and consistently handle repetitive tasks. Here’s how RPA supports companies in staying compliant with IFRS.
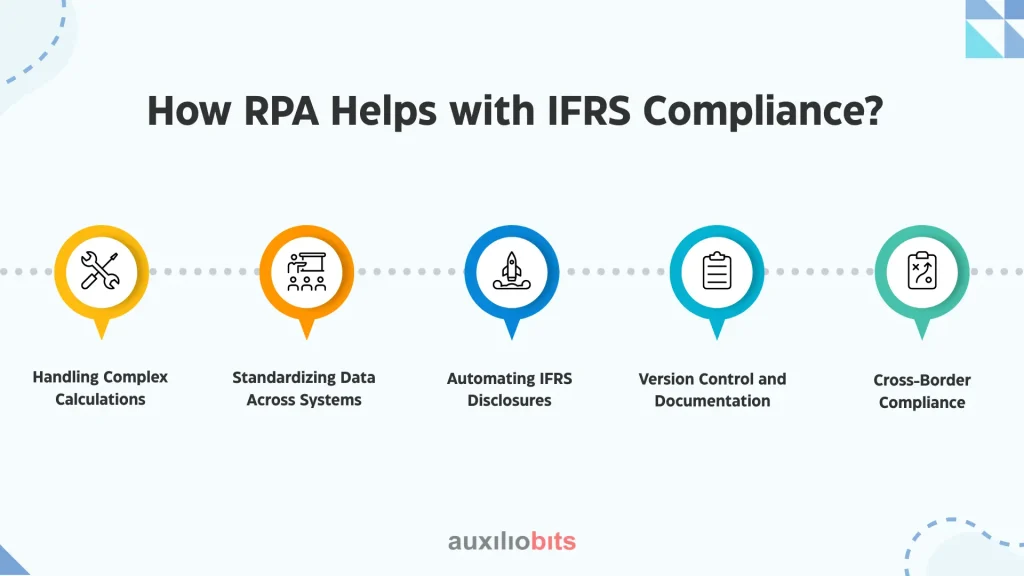
1. Handling Complex Calculations
IFRS often involves advanced calculations that go beyond basic accounting. This includes things like:
- Lease liability calculations
- Revenue recognition based on performance obligations
- Asset impairment testing
These tasks require pulling data from different systems, applying specific formulas, and documenting the results correctly.
RPA bots can:
- Gather necessary data from various internal systems like ERP, CRM, or spreadsheets
- Perform the required calculations using predefined rules and logic.
- Save the results along with the methods and assumptions.
This reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and ensures the same approach is used every time, which is key for IFRS compliance.
2. Standardizing Data Across Systems
Many businesses use multiple accounting, billing, payroll, and reporting systems, making keeping data consistent and aligned with IFRS rules challenging.
RPA helps by:
- Pulling data from different systems (even older or legacy software)
- Converting it into a standardized format
- Feeding it into the financial reporting tools
This ensures that reports are uniform and comparable, which aligns with IFRS’s goal of consistency across entities and countries.
3. Automating IFRS Disclosures
IFRS requires companies to disclose detailed information about how they arrived at their financial numbers. These disclosures are as important as the numbers and must follow specific formats.
RPA can help by:
- Extracting required disclosure data from systems
- Automatically filling out standard disclosure templates.
- Attaching related documents, such as supporting spreadsheets or policy notes
This saves time and increases the accuracy and completeness of disclosures, which is especially helpful during audits or regulatory reviews.
4. Version Control and Documentation
Keeping track of accounting policies, changes in assumptions, and updates to reports is crucial for IFRS. Auditors and regulators often request documentation for past reporting periods.
RPA bots can:
- Track changes in financial data or assumptions
- Maintain version histories of financial reports.
- Store all documentation in an organized and searchable format.
This makes it easier for finance teams to respond quickly and confidently to audit queries.
5. Cross-Border Compliance
Multinational companies may find applying IFRS consistently across different countries and subsidiaries challenging. Other teams may interpret the standards differently.
RPA helps by:
- Applying the same automation logic and workflows across all regions
- Using shared templates and formats for reporting and documentation
- Ensuring consistent application of IFRS policies, no matter where the data comes from
This standardization improves global compliance and reduces the risk of errors or inconsistencies.
RPA is a valuable tool for helping companies meet the demands of IFRS. It reduces manual work, increases accuracy, and ensures consistency across systems and countries. By automating complex calculations, disclosures, and documentation, RPA helps finance teams stay compliant, efficient, and audit-ready.
Real-World Use Cases
Here are a few real-world scenarios where RPA helps with compliance:
| Use Case | RPA Role |
Journal entry review | RPA checks all journal entries for completeness, accuracy, and approval. |
Balance sheet reconciliations | Bots reconcile accounts across systems and flag mismatches. |
Expense policy compliance | RPA scans expense reports to ensure they match company policies. |
Financial close | Bots automate data collection, calculations, and preliminary report generation. |
Audit support | RPA provides audit trails and retrieves documentation on demand. |
Key Benefits of Using RPA for Compliance
Here’s a quick summary of how RPA helps finance teams meet SOX and IFRS standards:
| Benefit | Description |
| Accuracy | Eliminates human errors in financial data |
| Speed | Speeds up reporting and reconciliation tasks |
| Consistency | Applies rules and controls uniformly |
| Auditability | Creates detailed logs and audit trails |
| Scalability | Handles large volumes of data with ease |
| Cost Savings | Reduces manual effort and compliance costs |
Getting Started with RPA: Tips for Finance Teams
1. Identify Repetitive and Rule-Based Tasks
The first step is to find the right tasks to automate. RPA works best on jobs that are:
- Repetitive (done the same way every time)
- Rule-based (follow a clear set of steps or decisions)
- Time-consuming (takes up a lot of employee hours)
For example, tasks like copying data from one system to another, checking for missing invoices, or matching transactions with policies are perfect for automation—list such functions in your daily, weekly, or monthly work routines.
2. Map Your Compliance Workflows
Before you build any bots, it’s essential to understand your compliance processes. Look at how financial rules—like SOX or IFRS—apply to your team’s work. What are the steps involved in ensuring compliance? Who is responsible for what? Where are the risks?
Creating a simple process map or checklist helps you see where RPA can have the most impact. It also ensures that automation supports, rather than disrupts, your existing workflows.
3. Choose the Right RPA Tool
There are many RPA tools available, but not all are the same. Popular platforms include:
- UiPath – Easy to use and suitable for complex automation.
- Automation Anywhere—Offers cloud and on-premises options.
- Microsoft Power Automate – Great if you already use Microsoft 365.
When choosing a tool, consider factors like ease of use, cost, support, and how well it integrates with your existing systems (like ERP, accounting software, etc.).
4. Start Small with Simple Bots
While automating everything at once is tempting, starting small is better. Pick one or two simple automated processes, like generating a daily report or checking for duplicate payments.
Building small bots first helps your team learn how RPA works, test results, and fix issues more easily. Once you gain confidence and see the benefits, you can move on to more advanced tasks.
5. Involve Audit and Compliance Teams
Your audit and compliance teams are key stakeholders. Involve them early in your RPA projects. They can help you:
- Make sure bots follow regulatory rules
- Validate that controls are working correctly.
- Ensure audit trails are maintained.
This teamwork builds trust and avoids problems later on during internal or external audits.
6. Monitor and Improve
Once your bots are up and running, don’t just set them and forget them. Review their performance regularly.
- Are they doing the job correctly?
- Are there any changes in the process or regulations?
- Could the bot be improved?
Update and maintain bots as needed to keep them effective and compliant. Good monitoring ensures your RPA solution continues to support your compliance goals.
Starting with RPA doesn’t have to be hard. By taking small steps and focusing on the right processes, your finance team can use RPA to stay compliant, reduce stress, and work more efficiently.
Conclusion
Compliance with SOX and IFRS is not just a checkbox—it’s essential for building trust, avoiding fines, and running a transparent business. However, compliance can also be complex and time-consuming.
Robotic process automation offers an innovative solution. By taking over repetitive tasks, ensuring accuracy, and providing reliable audit trails, RPA helps finance teams meet regulatory requirements with confidence and efficiency.
As technology evolves, RPA will play an even bigger role in modern finance departments—helping them stay compliant, efficient, and future-ready.