Key Takeaways
- APA proactively detects and resolves issues before they escalate, thereby minimizing disruptions, improving system reliability, and enhancing the customer experience across critical business operations.
- Autonomous AI agents continuously monitor environments, analyze patterns, and act with minimal human input, providing seamless automation and enabling real-time decision-making and system recovery.
- Machine learning and predictive maintenance reduce downtime, enabling businesses to identify and address potential issues proactively, thereby saving operational costs and preventing workflow interruptions.
- NLP and RPA integration enhance communication and accuracy, allowing users to interact naturally with systems while ensuring repetitive tasks are performed quickly, consistently, and without errors.
- APA builds resilient, self-healing infrastructures that can automatically manage incidents and learn from past events to prevent future system failures and reduce human error dependencies.
One of the most vital challenges modern business settings face is operational downtime. Even a few minutes of unplanned downtime can give rise to serious issues, leading to consequences nobody wants to face. Traditional approaches to managing downtime often rely on manual actions and reactive assistance, which are slow and lack consistency. Moreover, these methods struggle to keep pace with the rapid growth and complexity of today’s businesses. To effectively tackle this issue, organizations should adopt agentic process automation to realize its full advantages.
There is no doubt that by utilizing artificial intelligence agents, APA marks a paramount milestone in workplace automation. Departments such as customer service, finance, manufacturing, and IT operations can leverage AI agents to identify anomalies, take immediate action, and enhance overall performance without delay.
What makes agentic process automation effective in lessening downtime is its adaptive and proactive nature. APA agents can monitor continuously. For example, an APA-driven system can identify early warning signs of a server overload and initiate maintenance before any mishap occurs. Additionally, in sectors where customer service is paramount, agentic process automation ensures that no question remains unanswered.
As enterprises face various challenges of digital transformation, APA provides a solution to ensure that businesses continue to grow while addressing the challenges they encounter. This reduces operational risks and ensures that all aspects meet the required standards.
Also read: Cooperative vs. Competitive AI Agents: Strategic Frameworks for Business Process Automation.
Understanding Agentic Process Automation
Agentic process automation leverages the power of artificial intelligence and robotic process automation, utilizing autonomous AI agents to drive efficiencies. Because firms continually strive to offer the best services and products in a changing market, APA provides a strong foundation for developing innovative and proactive systems that deliver more benefits compared to conventional automation. Unlike traditional robotic process automation, which operates based on pre-set guidelines, APA employs a more sophisticated approach to automation. It not only enables agents to perform tasks but also ensures that they consider the requirements and then act with minimal human intervention. This is one primary reason why firms should consider APA to lessen downtime.
Core Components of APA
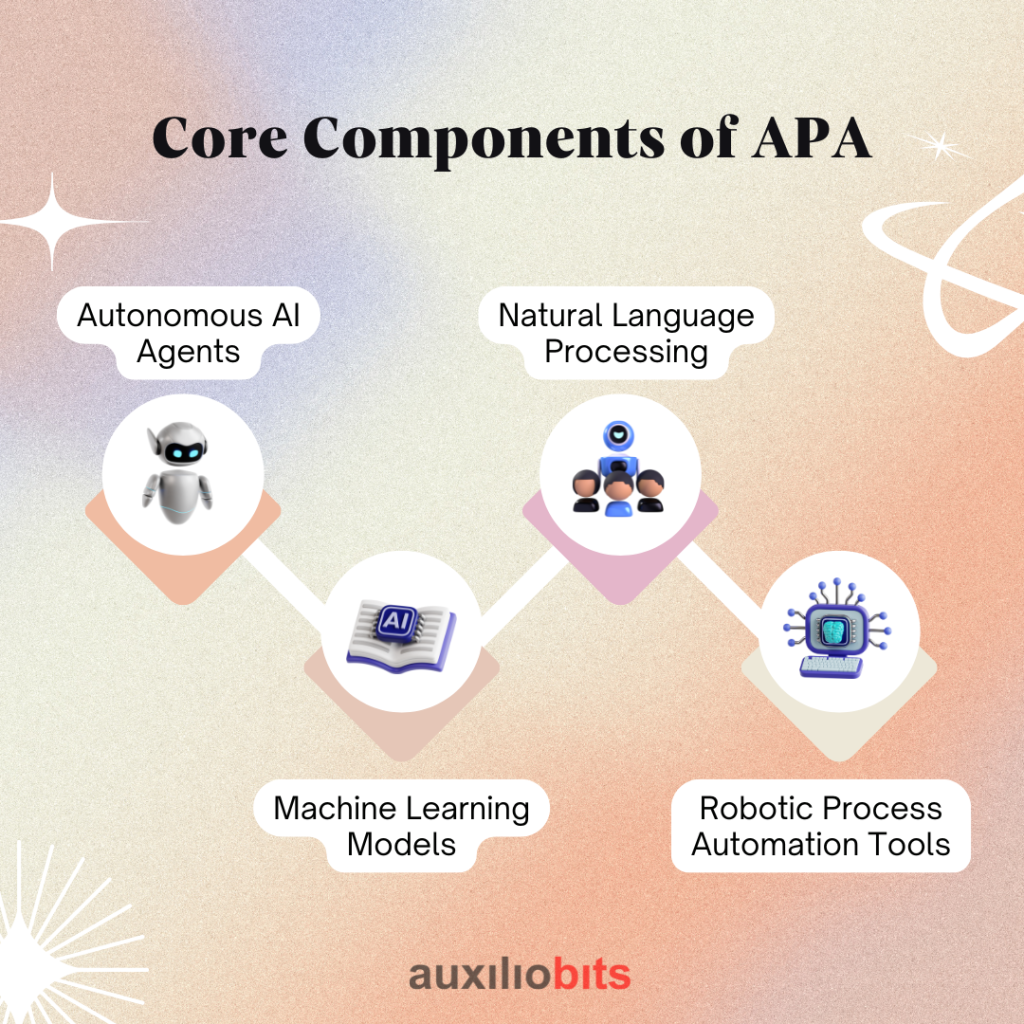
1. Autonomous AI Agents
Studies say that autonomous AI agents are the foundation of agentic process automation. These independent agents are designed to operate autonomously. From understanding changing environments and then taking immediate actions, APA will never disappoint firms if used wisely. It has the potential to consider the challenges of several workflows and recommend a suitable solution. For example, in an IT department, an autonomous agent can ensure that no employee suffers due to system issues. It offers continuity without any human assistance. Furthermore, it also ensures that technical glitches are sorted.
2. Machine Learning Models
Machine learning models are trained to optimize decision-making, identify issues, and identify patterns. For example, an ML model can determine when a component is likely to fail. This enables firms to schedule maintenance in advance, ensuring that no future challenges arise. This outcome reduces downtime and saves money.
3. Natural Language Processing
NLP allows agentic process automation systems to interpret and respond to human language. This is one primary reason why they are more user-friendly. With natural language processing, it becomes easier to interact with AI systems. Whether you are submitting requests or asking questions, NLP ensures a smooth interaction with the systems. Therefore, as a result, user experiences get better, especially in sectors where communication plays a crucial role.
4. Robotic Process Automation Tools
RPA is one of the most critical components of agentic process automation, particularly when managing tasks that do not require cognitive decision-making. RPA tools ensure speed, consistency, and accuracy in a wide range of processes, including report generation and system updates. When integrated with artificial intelligence and AI agents, RPA plays a crucial role and is capable of adjusting workflows.
How APA Reduces Downtime?
Agentic process automation is designed to enhance operational resilience by proactively addressing the causes of downtime. By combining artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation, APA enables enterprises to shift from reactive recovery to predictive, real-time, and self-sustaining operations. Below are the key ways APA reduces downtime and ensures uninterrupted business continuity:

1. Predictive Maintenance
APA leverages machine learning to continuously monitor system health by analyzing real-time sensor inputs, application logs, and historical performance data. Instead of waiting for a failure to occur, APA identifies early warning signs—such as abnormal temperature, vibration, or latency—and predicts when equipment or software is likely to malfunction.
Example: In a manufacturing setup, APA can monitor vibration patterns of rotating machinery to detect signs of bearing wear. When anomalies are detected, the system alerts technicians and schedules proactive maintenance, preventing unplanned shutdowns and costly repairs.
2. Real-time Monitoring and Alerts
APA agents provide 24/7 monitoring of infrastructure, applications, and user activity. These agents detect deviations from normal behavior, such as memory leaks, CPU spikes, or unusual network traffic, and respond in real time. They assess the severity of issues and follow predefined rules to auto-resolve simple problems or escalate critical incidents.
Example: When a web server experiences a sudden memory surge, an APA agent can automatically clear the cache, restart services, or allocate additional resources from the cloud, thereby mitigating service disruption without requiring human intervention.
3. Automated Incident Response
Rather than relying on IT teams to manually address incidents, APA triggers automated recovery workflows as soon as an issue arises. These workflows may include rolling back faulty updates, initiating failover mechanisms, or running remediation scripts to restore normalcy quickly.
Example: If a banking application’s payment gateway goes offline, APA detects the outage, reroutes traffic to a backup gateway, and notifies administrators, ensuring customers can continue transactions seamlessly.
4. Human Error Mitigation
APA significantly reduces the risk of human error by automating repetitive, rule-based, and high-stakes tasks. It also guides users through complex procedures using contextual recommendations, validation rules, and error-checking mechanisms.
Example: In a data entry process, APA can validate entries in real time, such as checking for duplicate invoice numbers or invalid customer IDs, helping users correct errors instantly before they cause downstream issues.
5. Intelligent Decision-Making
APA agents are equipped with decision-making capabilities that allow them to analyze multiple data inputs, consider business rules, and take appropriate actions autonomously. This rapid, informed response ensures minimal delay in reacting to operational anomalies or threats.
Example: During a cyberattack, APA can detect suspicious traffic, analyze its origin and behavior, isolate affected nodes, and apply firewall rules—without waiting for manual security team intervention.
6. Self-Healing Systems
The most transformative aspect of APA is its ability to enable self-healing systems. APA agents can diagnose recurring issues, identify root causes, and apply corrective measures based on historical resolutions and learned behavior.
Example: If an application crashes due to a memory leak, APA pinpoints the problem to a specific module, reconfigures memory settings, and automatically redeploy the application, preventing further downtime without requiring any developer involvement.
By incorporating APA into core operations, organizations can move towards a truly resilient, intelligent infrastructure that anticipates problems, acts swiftly, and continuously evolves, ensuring that downtime becomes a rarity rather than a recurring threat.
Conclusion
Operational downtime can no longer be tolerated as a sane inefficiency. In a fast-paced, digital-first world, enterprises must aim for zero disruption. Agentic Process Automation provides the intelligence, speed, and autonomy needed to achieve this goal. By proactively identifying issues, automating resolutions, and continuously optimizing operations, APA significantly reduces downtime, ensuring that businesses stay resilient, agile, and competitive.
Organizations that invest in APA not only safeguard their operations but also position themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly automated future.








