Key Takeaways
- Computer vision is a digital assistant for doctors. It helps them read complex medical images faster and more accurately by detecting patterns and abnormalities invisible to the human eye.
- AI tools trained on thousands of images can more efficiently diagnose diseases like cancer, pneumonia, and fractures, enabling quicker, more accurate treatment planning and improved patient outcomes.
- Computer vision enhances early diagnosis capabilities, identifying illnesses at their earliest stages. This allows patients to begin treatment sooner and potentially avoid severe complications.
- It brings diagnostic power to underserved areas, supporting healthcare providers in rural clinics or small hospitals that lack access to specialized radiologists or advanced imaging resources.
- By automating image analysis and reporting, computer vision reduces doctors’ workload, minimizes costs, and improves consistency in care without replacing the essential role of human judgment
Your health is of utmost importance. Regardless of the health concern, visiting a doctor immediately is recommended. Over time, patients face several challenges when planning to see a doctor. From scheduling appointments to opting for an MRI, there’s always something going on. On the other hand, even medical professionals have so much on their plates. From making sure that all the patients are attended to identifying the health concern, doctors are under constant pressure.
One of the most critical challenges for doctors is identifying the readings in diagnostic imaging, like CT scans. There are times when human eyes cannot identify the health problem, no matter the doctor’s experience. Henceforth, one suitable solution for such a challenge is computer vision. It is an up-and-coming technology that has changed the medical industry. It has allowed doctors to understand the readings on diagnostic images and ensured that every small detail is visible to the human eye. The doctors can easily monitor the patient’s situation and check if they need immediate attention.
At present, computer vision is utilized in every medical setting and clinic. It allows doctors to diagnose major health concerns, including lung infections, tumors, and broken bones. Additionally, it was used to help screen for cancer, diabetes, and COVID-19. In many situations, it worked better than doctors and lessened the chances of human mistakes.
Also read: Synthetic Data Generation for Healthcare AI Training: Techniques and Privacy Considerations.
What Is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that helps computers “see” and understand images or videos. Just like humans use their eyes and brains to recognize things, computers use cameras and smart algorithms to recognize objects and patterns in pictures.
Computer vision works by analyzing the details in an image. It looks at colors, shapes, edges, and textures. Then it compares those features with what it has learned before. Over time, the computer gets better at recognizing what it is seeing. It learns from thousands or even millions of example images.
In healthcare, computer vision is mainly used to look at medical images. These images show what’s happening inside the human body. Some common types of medical images include
- X-rays—used to see bones and lungs
- MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) are used to see soft tissues like the brain or muscles.
- CT scans (Computed tomography) are used to see detailed images of organs.
- Ultrasounds—used to see moving images of organs or babies in the womb
- PET scans are used to check how organs and tissues are working.
Doctors use these images to spot problems such as:
- Tumors (unusual growths)
- Bone fractures
- Infections
- Organ damage
- Diseases like cancer or pneumonia
Computer vision helps by quickly finding signs of these problems. It acts like a smart assistant for the doctor, highlighting areas that may need closer examination. This makes it easier and faster for doctors to diagnose patients.
Computer vision does not replace doctors. Instead, it helps them make better and faster decisions, improve accuracy, and reduce mistakes, which can lead to better patient care.
How Is Computer Vision Used in Diagnostic Imaging Today?
Computer vision plays a significant role in modern healthcare, especially diagnostic imaging. It helps doctors read and understand medical images more quickly and accurately. Let’s look at some of the main ways it is being used today:
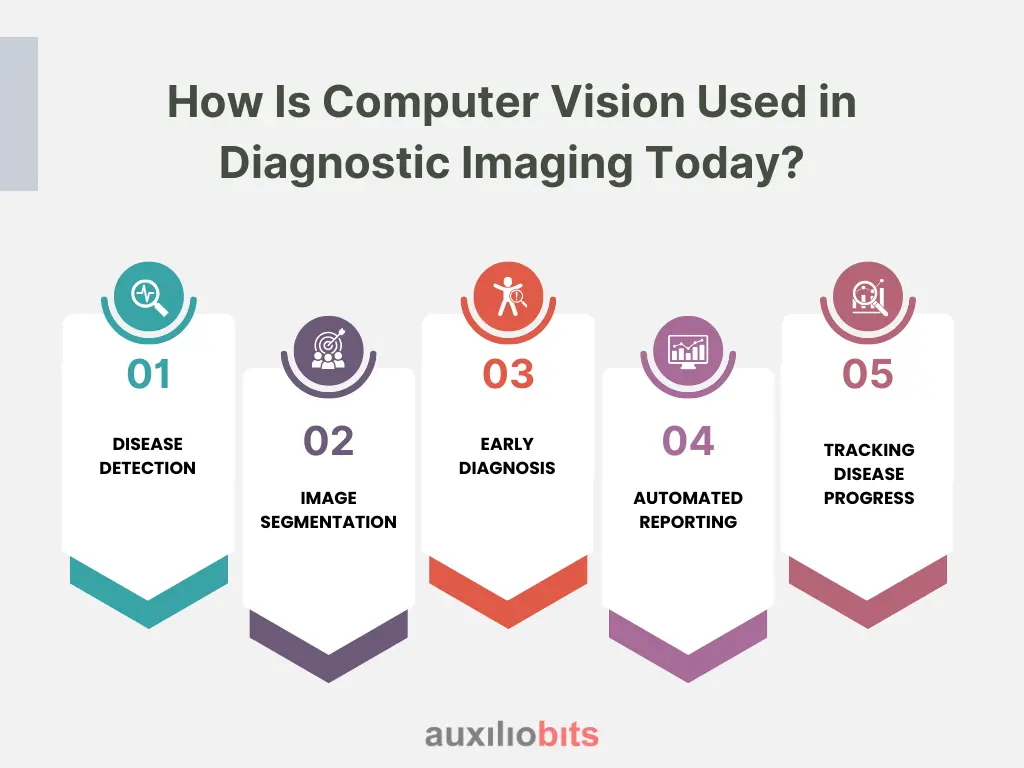
1. Disease Detection
One of computer vision’s most common uses is to detect disease signs in medical images. For example:
- It can find lung cancer in chest X-rays or CT scans.
- It can detect breast cancer in mammograms.
- It can spot brain tumors in MRI scans.
- It can identify COVID-19 pneumonia in chest X-rays.
These AI systems are trained on thousands of medical images. They learn to recognize patterns that are linked to certain diseases. Sometimes, they can even see things that a human eye might miss. This helps doctors find health problems earlier and more accurately
2. Image Segmentation
Computer vision can divide a medical image into parts. This is called image segmentation. For example, in a brain scan, the tool can highlight the area where a tumor is located. It shows the exact size, shape, and position of the problem. This helps doctors plan surgeries or treatments with better precision.
3. Early Diagnosis
Computer vision can spot signs of disease very early, even before the patient shows symptoms. Catching diseases early can save lives. It also helps avoid expensive and complex treatments later on. For instance, early signs of diabetic eye disease or cancer can be detected before they become severe.
4. Automated Reporting
Some computer vision tools can automatically create medical reports. They describe what was found in the image and suggest possible next steps. This saves time for radiologists and reduces the chance of missing something important. It also ensures that the same standards are followed for every patient.
5. Tracking Disease Progress
Computer vision can compare medical images taken at different times. It can tell whether a tumor has grown, if an infection is healing, or if a bone fracture is improving. This helps doctors know if a treatment is working or changes are needed.
Benefits of Using Computer Vision in Imaging
Computer vision brings many powerful benefits to healthcare, especially in medical imaging. It is not just about using new technology—improving patient care, saving time, and reducing costs. Let’s take a closer look at how computer vision helps:
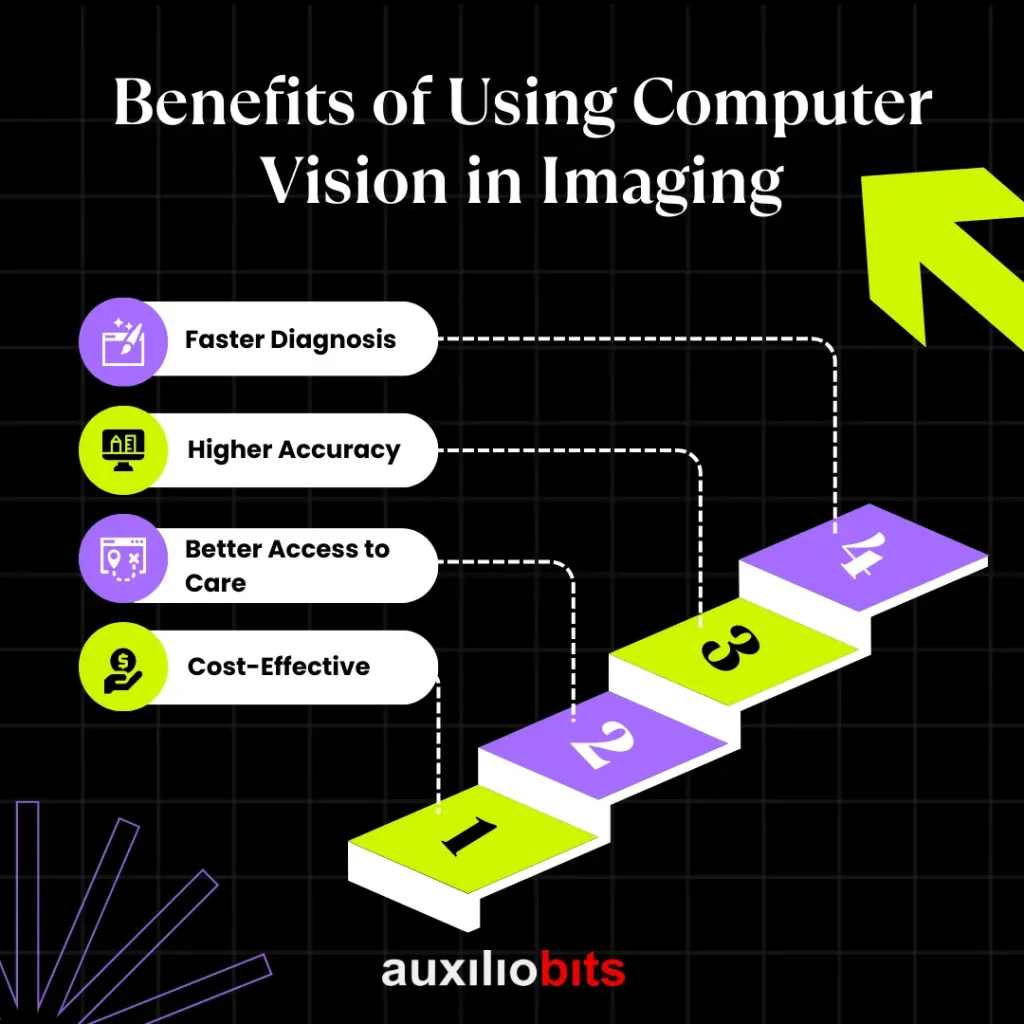
1. Faster Diagnosis
One of the most significant benefits of computer vision is speed. Medical images like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans can take a long time to analyze manually. A radiologist may need several minutes—or even hours—to study a single scan. But computer vision tools can explore thousands of images within minutes. This speed helps in emergencies, like stroke or internal bleeding, where every second counts. Faster results mean quicker treatment and better outcomes for patients.
2. Higher Accuracy
Even skilled doctors can make mistakes, especially when tired or overloaded with work. Computer vision does not get tired. It follows a set of trained rules and patterns and can spot even the most minor signs of disease. In many cases, AI tools have matched or even surpassed human experts in detecting conditions like cancer or pneumonia in medical images. This high level of accuracy helps reduce the chances of missed diagnoses or false alarms. It acts as a second pair of expert eyes, supporting doctors in making the right decisions.
3. Better Access to Care
Not every hospital or clinic has experienced radiologists. This is especially true in rural or remote areas. With computer vision, even small hospitals or clinics can get support from advanced diagnostic tools. These tools can help doctors in remote locations give the same level of care as big hospitals in cities. This leads to more equal access to healthcare for all patients, no matter where they live.
4. Cost-Effective
Healthcare can be expensive. Hospitals can save both time and money by using computer vision to automate parts of the diagnostic process. For example, automatically generating reports or pre-screening images helps reduce the workload for doctors and avoids extra tests. Over time, this can lead to lower healthcare costs for hospitals and patients without lowering the quality of care.
Conclusion
Computer vision is changing the way we diagnose diseases. This technology is transforming medical imaging from spotting tumors in seconds to helping doctors make better decisions. While there are still challenges, the future looks promising with smarter, faster, and more reliable tools on the horizon.
In simple words, computer vision is helping doctors “see” better and sooner, making healthcare safer and smarter for everyone.








