Key Takeaways
- Inventory holding costs can eat up 15–30% of your inventory’s value annually, including capital, storage, service, and risk-related expenses, making them a critical cost center to optimize.
- AI agents drastically improve demand forecasting accuracy by analyzing historical, external, and real-time data, reducing overstocking and understocking issues that inflate holding costs.
- Automation powered by AI agents enables self-managing inventory systems, optimizing replenishment, stock levels, and supplier decisions without human intervention, significantly cutting labor and operational costs.
- Smart warehouses powered by AI streamline layout, movement, and fulfillment processes using predictive analytics, robotics, and route optimization, leading to lower space utilization and faster inventory turnover.
- Businesses adopting AI for inventory management report 15–25% operational cost reductions and a positive ROI within 6–18 months, making AI not just a tech upgrade, but a strategic imperative for profitability.
The global supply chain is a complex, interconnected web, constantly evolving and facing myriad challenges, from geopolitical shifts to sudden demand fluctuations. Effective coordination across diverse supply chain teams—procurement, logistics, manufacturing, sales, and more—is paramount for resilience and efficiency. Traditional methods often fall short, leading to silos, miscommunication, and slow decision-making.
So what works best here? CrewAI, a powerful framework for building multi-agent AI systems that promises to revolutionize how these teams operate and collaborate.
Also read: Blockchain Integration with AI Agents for Supply Chain Transparency.
The Intricacies of Supply Chain Coordination
Supply chains, by nature, involve a multitude of stakeholders, processes, and data points. Coordinating these elements effectively is a monumental task.
Traditional Challenges in Supply Chain Collaboration
- Information Silos:
Different departments often use disparate systems, leading to fragmented data and a lack of a unified view of the supply chain. This hinders real-time decision-making. - Demand Volatility and Forecasting Inaccuracies:
Predicting consumer demand is notoriously difficult. Inaccurate forecasts lead to either excess inventory (tying up capital) or stockouts (lost sales and customer dissatisfaction). The “bullwhip effect” further amplifies these fluctuations upstream in the supply chain. - Supplier Coordination Complexities:
Managing relationships with numerous suppliers, negotiating contracts, tracking lead times, and ensuring timely deliveries are constant challenges, especially in just-in-time (JIT) environments. - Logistics and Transportation Hurdles:
Optimizing routes, managing carriers, and navigating unexpected delays due to traffic, weather, or port congestion can severely impact delivery schedules and costs. - Risk Management and Resilience:
Modern supply chains are susceptible to a wide range of disruptions, from natural disasters and pandemics to geopolitical tensions. Proactive risk identification and mitigation require seamless collaboration. - Manual Processes and Human Error:
Many supply chain tasks still rely on manual data entry, approvals, and communication, making them prone to errors, delays, and inefficiencies. - Cultural and Organizational Differences:
In global supply chains, harmonizing diverse work practices, languages, and cultural norms across international teams and partners adds another layer of complexity.
These challenges underscore the urgent need for more sophisticated, integrated, and intelligent solutions to foster truly collaborative and efficient supply chain operations.
Introducing CrewAI: A Paradigm Shift in Team Coordination
CrewAI is an innovative open-source framework designed to build and orchestrate multi-agent AI workflows. Unlike single-AI solutions, CrewAI enables the creation of “crews” of specialized AI agents that can communicate, collaborate, and delegate tasks to achieve complex objectives. This framework is particularly well-suited for scenarios requiring coordinated intelligence, making it a game-changer for supply chain management.
Core Concepts of CrewAI Architecture
At its heart, CrewAI operates on several key principles:
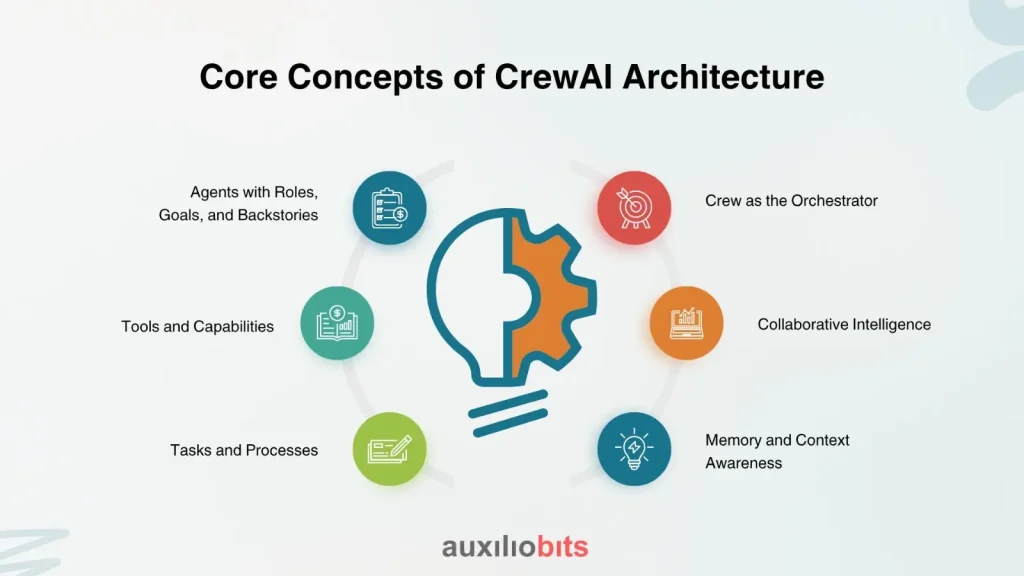
- Agents with Roles, Goals, and Backstories: Each AI agent within a CrewAI system is assigned a specific role (e.g., “Demand Forecasting Analyst,” “Procurement Specialist,” “Logistics Coordinator”), a clear goal (e.g., “Minimize inventory holding costs,” “Ensure on-time delivery”), and a backstory (contextual information that guides its behavior and decision-making). This role-based design mimics human teams, allowing for specialization and efficient task allocation.
- Tools and Capabilities: Agents are equipped with specific tools (e.g., APIs, databases, external systems) that enable them to interact with the real world, gather data, execute actions, and perform their assigned tasks.
- Tasks and Processes: Individual tasks are defined with clear objectives and expected outputs. A Process orchestrates how these tasks are executed among agents, defining collaboration patterns (e.g., sequential, hierarchical, or parallel workflows).
- Crew as the Orchestrator: The “Crew” is the top-level entity that manages the entire team of AI agents, oversees workflows, ensures seamless collaboration, and ultimately delivers the desired outcomes. It’s akin to a project manager, ensuring all parts of the operation work in concert.
- Collaborative Intelligence: CrewAI facilitates real-time communication and information sharing between agents, allowing them to collectively reason, plan, and execute tasks, breaking down the traditional silos found in human-only operations. Agents can share insights, provide feedback, and even delegate sub-tasks to other specialized agents.
- Memory and Context Awareness: Agents maintain persistent context and memory across steps, allowing them to “remember” past decisions, rationale, and shared data. This is crucial for long-running or complex supply chain workflows where context is vital.
This modular and collaborative architecture empowers businesses to build sophisticated, autonomous AI applications that can tackle complex, multi-faceted problems, much like a well-coordinated human team.
CrewAI in Action: Revolutionizing Supply Chain Coordination
The application of CrewAI in supply chain management offers transformative potential across various functions.
Enhanced Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
Agent Roles:
- Market Analyst Agent: Gathers real-time market data, economic indicators, and competitor activities using web scraping tools and market intelligence APIs.
- Sales Data Analyst Agent: Analyzes historical sales data, promotional impacts, and seasonal trends from internal ERP/CRM systems.
- Forecasting Agent: Combines insights from both agents, leveraging machine learning models to generate highly accurate demand forecasts, considering various influencing factors.
- Inventory Optimization Agent: Based on forecasts and current stock levels, recommends optimal inventory levels, reorder points, and safety stock, minimizing holding costs while preventing stockouts.
- Collaboration: The Market Analyst feeds external insights to the Forecasting Agent, while the Sales Data Analyst provides internal historical data. The Forecasting Agent then generates predictions, which the Inventory Optimization Agent uses to formulate concrete recommendations.
Streamlined Procurement and Supplier Management
Agent Roles:
- Procurement Research Agent: Identifies potential new suppliers, researches their capabilities, compliance, and sustainability records.
- Negotiation Assistant Agent: Provides real-time market pricing data, historical negotiation outcomes, and supplier performance metrics to human procurement teams, or even conducts initial automated negotiations for simple transactions.
- Supplier Onboarding Agent: Automates the collection of supplier documentation, validates information, and integrates new suppliers into the system, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Performance Monitoring Agent: Continuously tracks supplier performance against KPIs (lead time, quality, delivery adherence), flagging deviations and recommending corrective actions.
- Collaboration: The Procurement Research Agent feeds qualified leads to the Negotiation Assistant, which in turn might pass details to the Onboarding Agent. The Performance Monitoring Agent provides continuous feedback to all relevant agents and human managers.
Optimized Logistics and Transportation
Agent Roles:
- Route Optimization Agent: Analyzes real-time traffic, weather, road conditions, and delivery schedules to propose the most efficient transportation routes.
- Carrier Selection Agent: Evaluates carrier performance, cost, and availability to recommend the best option for specific shipments.
- Shipment Tracking Agent: Monitors shipments in real-time, provides proactive alerts on delays or deviations, and updates relevant stakeholders.
- Customs & Compliance Agent: Handles necessary documentation for international shipments, ensuring adherence to regulations and minimizing delays at borders.
- Collaboration: The Shipment Tracking Agent informs the Route Optimization Agent of any real-time issues, which can then suggest alternative paths. All agents share data to ensure smooth, compliant, and cost-effective delivery.
Proactive Risk Management and Resilience Building
Agent Roles:
- Risk Identification Agent: Scans news, geopolitical reports, weather forecasts, and social media for potential disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, strikes, port closures).
- Impact Assessment Agent: Analyzes potential impacts of identified risks on inventory, production, and delivery schedules.
- Contingency Planning Agent: Based on impact assessments, suggests alternative suppliers, routes, or production plans.
- Communication Agent: Drafts alerts and updates for relevant internal teams and external partners regarding potential disruptions and mitigation strategies.
- Collaboration: The Risk Identification Agent continuously feeds information to the Impact Assessment Agent. Once an impact is determined, the Contingency Planning Agent is activated, and its recommendations are disseminated by the Communication Agent.
Automating Routine Tasks and Enhancing Customer Service
Agent Roles:
- Order Processing Agent: Automates the entry and validation of customer orders, reducing manual intervention.
- Customer Inquiry Agent: Responds to common customer queries regarding order status, shipping times, and product availability.
- Issue Resolution Agent: Identifies and categorizes supply chain issues (e.g., delayed shipments, damaged goods) and routes them to the appropriate human or AI agent for resolution.
- Collaboration: The Customer Inquiry Agent can escalate complex queries to human customer service representatives or consult with the Shipment Tracking Agent for real-time updates.
Implementing CrewAI: Key Considerations
Adopting Crew AI architecture requires careful planning and execution.
1. Data Integration is Paramount
CrewAI agents are only as effective as the data they can access. A robust data infrastructure that allows for seamless integration with ERP systems, WMS (Warehouse Management Systems), TMS (Transportation Management Systems), CRM, IoT devices, and external data sources (e.g., market data, weather APIs) is crucial. Data quality and consistency must be prioritized.
2. Defining Agent Roles and Tasks
The success of a CrewAI implementation hinges on precisely defining the roles, goals, and backstories of each agent and breaking down complex supply chain processes into manageable, well-defined tasks. Ambiguity can lead to suboptimal performance.
3. Choosing the Right LLMs and Tools
Selecting appropriate Large Language Models (LLMs) for powering the agents is essential, considering factors like cost, performance, and specific task requirements. Integrating the right external tools (APIs, custom scripts, databases) that enable agents to perform their functions is equally important.
4. Iterative Development and Testing
Implementing CrewAI should follow an iterative approach. Start with a smaller, well-defined use case, build and test the crew, gather feedback, and then expand to more complex scenarios. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of agent performance are vital for refinement.
5. Human-in-the-Loop Strategy
While CrewAI promotes autonomy, a “human-in-the-loop” approach is often necessary, especially in critical decision points or for handling exceptions. AI agents should augment human capabilities, not entirely replace them. This ensures oversight, builds trust, and allows for human intuition and complex problem-solving where AI might still fall short.
6. Scalability and Infrastructure
Consider the computational resources required to run multiple AI agents concurrently, especially as the system scales. Cloud-based infrastructure and robust deployment strategies will be key.
7. Security and Data Privacy
Given the sensitive nature of supply chain data, ensuring data security and privacy within the CrewAI architecture is non-negotiable. Implement strong access controls, encryption, and compliance with relevant regulations.
The Future of Supply Chain with CrewAI
As supply chains continue to become more complex and data-intensive, the role of intelligent automation and collaborative AI systems like CrewAI will undoubtedly grow. By enabling specialized AI agents to work together seamlessly, CrewAI offers a powerful solution for overcoming the traditional challenges of supply chain coordination.
From optimizing inventory and streamlining procurement to enhancing logistics and building resilience against disruptions, CrewAI architecture promises a more efficient, agile, and robust future for supply chain management. Embracing such innovative AI frameworks won’t just improve operational efficiency; it will foster a new era of collaborative intelligence, turning complex supply chain networks into highly synchronized, self-optimizing ecosystems.








