Key Takeaways
- RPA complements EMR systems like eClinicalWorks, ModMed, and SimplePractice by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks such as scheduling, billing, and patient intake.
- Efficiency and accuracy improve dramatically when bots handle data entry, reminders, and claims processing, reducing errors and freeing staff to focus on patient care.
- **Challenges exist—**including setup costs, staff training, and bot maintenance—but careful planning and change management can mitigate these barriers.
- RPA has limitations, particularly in tasks requiring human judgment, creativity, or decision-making, making it best suited for high-volume, repetitive processes.
- Healthcare practices can achieve better patient experiences and cost savings by integrating RPA with EMRs, ultimately creating more scalable and patient-centric workflows.
The healthcare industry is transferring patient care to modern, skilled systems, from scheduling appointments to dealing with billing. Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems such as eClinicalWorks, ModMed, and SimplePractice are central for this change, as patients organize data and well-organized operations. However, repetitive tasks such as data entry and appointment scheduling still burden employees.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) provides a solution by acting as a digital assistant. The RPA automatically automates regular tasks, such as entering the patient’s information, managing bills, and sending reminders, freeing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care. By integrating with EMR, RPA increases efficiency, reduces errors, and improves the overall experience for both employees and patients. This blog states how RPA EMR works with its benefits, challenges, boundaries, and practical applications.
Also read: EMR Integration Using LangChain and OpenAI for Smart Data Entry
What is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software that mimics human functions to perform repeated computer functions. Think of it as a virtual assistant who tirelessly handles tasks such as copying the data, clicking buttons, or filling out the form without errors. Unlike complex software integration, RPA works on the surface of existing programs, such as EMR, and requires minimal changes in current systems. For example, an RPA bot can log into an EMR. Remove the data as a patient, and input it in the right areas, following the pre-set rules. Its ability to operate 24/7 without fatigue makes it ideal for high-volume, repeated tasks in healthcare settings.
RPA in Healthcare
RPA is changing healthcare by automating the administrative tasks, saving time. This excels in environments where accuracy and speed are important, such as clinics and hospitals that use EMR systems. Here is how the RPA contributes:
- Repeat work automation: RPA handles tasks like entering patient data from a form to reduce manual work.
- Fast data processing: It processes large datasets quickly and reduces errors caused by human inspection.
- Notifications and Alerts: RPA sends automated alerts, such as informing employees about incomplete patient forms or system issues, ensuring smooth operation.
- Patient communication: This appointment manages the reminder, billing notice, and follow-up messages and improves patient engagement.
- Integration with other systems: RPA connects EMRs to external systems such as laboratories or insurance portals, streamlining workflows.
By handling these tasks, the RPA healthcare staff allows the patient to dedicate more time to taking care and making complex decisions.
RPA Benefits in EMR Integration
Integrating RPA with the EMR system provides important benefits for healthcare providers:
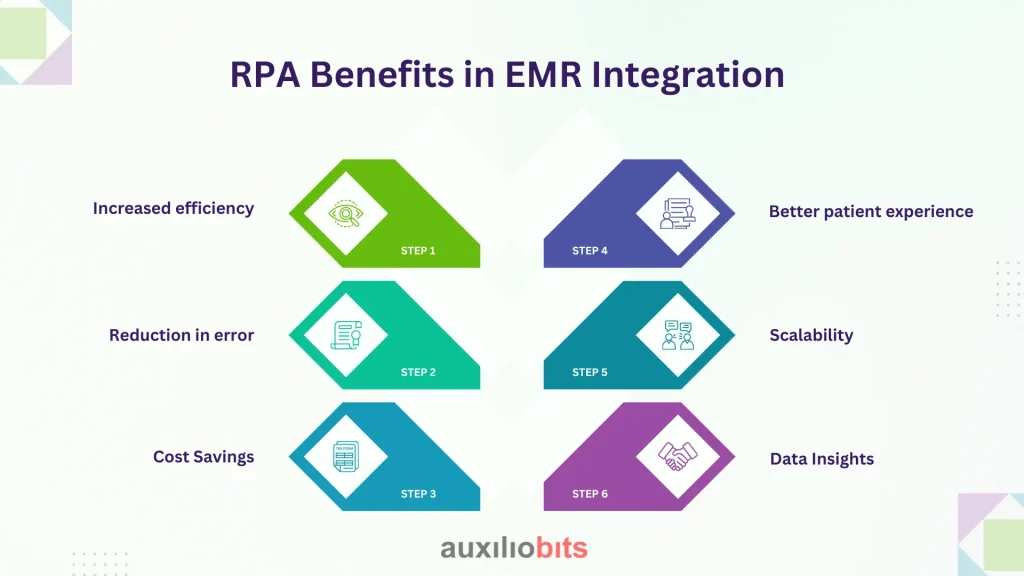
Increased efficiency:
RPA automatically saves the timing of repetitive tasks such as entry, scheduling, and billing, saving the time of employees. For example, a bot can process the patient’s intake forms in seconds compared to minutes for a human.
Reduction in error:
By eliminating manual data entry, the RPA reduces typos and incompatibility, ensuring accurate patient records and billing codes.
Cost Savings:
Automation reduces labor costs by reducing the need to do regular tasks, allowing clinic resources to be allocated more effectively.
Better patient experience:
Rapid check-in, accurate billing, and timely reminders increase the patient’s satisfaction and reduce no-shows.
Scalability:
RPA can handle raising the charge without additional employees, making it ideal for increasing practices
Data Insights:
RPA can compile data to the dashboard, providing insight into the patient’s volume, general diagnosis, or follow-up requirements, supporting the strategic plan.
These benefits make RPA a game-changer for healthcare practices, which are aimed at optimizing operations.
RPA Implementation Challenges
While RPA provides many benefits, applying it in healthcare comes with challenges:
Preliminary Setup Cost:
Software, training, and configuration are required to invest in and deploy RPA bots. Small practices can find it expensive.
Staff Training:
Employees require training to manage and monitor RPA bots, which may be time-consuming.
System compatibility:
While RPA works with existing systems, some EMRs may have unique interfaces that require custom bot configurations, adding complications.
Change Management:
Employees can oppose automation and fear job loss or unfamiliar technology. Apparent communication about the role of RPA as an assistant, not a replacement, is necessary.
Maintenance is needed:
Bots require regular updates to adapt to the EMR interfaces or workflows, which may demand ongoing technical support.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and cooperation with experienced RPA providers.
RPA Limits
RPA is powerful but not a cure. Its limitations include:
Only rules-based tasks:
RPA excels at repetitive and rule-based tasks but struggles with tasks that require complex decisions or human decisions, such as the diagnosis of patients.
Dependence on stable systems:
If an EMR interface changes (e.g., a button moves), the bot may fail as long as there is a need to monitor vigilance.
Data Safety concerns:
Although designed to secure RPA, any misunderstanding during the setup can put the data at risk, requiring strict compliance with HIPAA.
Limited creativity:
RPA may not be innovative or favorable beyond its programming, so it is not favorable for the functions requiring creativity or improvisation.
Scalability barriers:
While RPA is scalable, excessively high volume or highly customized workflows may require more advanced automation tools.
Understanding these boundaries helps clinics to determine realistic expectations for RPA.
Use Cases for RPA with EMR
The RPA can be applied to the patient’s journey, which increases the specific EMR systems, such as eClinicalWorks, ModMed, and SimplePractice. Here are practical examples:
ClinicalWorks
- Appointment Scheduling: RPA reads the patient’s requests from email or a web form and books appointments in EMR, and sends immediate confirmation.
- Data Integration: This lab results or patient portal draws data and enters the right patient chart, reducing manual work.
- Billing accuracy: RPA verifies the billing code and the patient’s information before submission, reducing claim rejection.
ModMed
- Voice-to-Text Integration: RPA transcribes doctors’ notes and populates them in a specific EMR field, which saves time for experts such as dermatologists.
- Inventory Management: It monitors medical supply levels in EMR and auto-generates orders when stocks are low.
- Patient follow-up: RPA sends post-procedure care instructions via email or SMS, and the patient improves compliance.
SimplePractice
- Client Onboarding: When a new client submits a web form, the RPA creates its profile, sends a welcome packet, and adds them to the scheduling system.
- Appointment Reminder: It sends automatic email or SMS reminders and reduces no-shows for the physician.
- Payment automation: Post-sessions, RPA stored credit cards pay using details and email receipts, streamlining billing.
Case of General Use
- Patient Check-in: RPA pre-EMR charts with data from online forms, allowing patients to verify the details on arrival.
- Insurance claims: It examines claims for errors, presents them to the insurance portals, and tracks their condition, only alerting employees to issues.
- Follow management: RPA records daily annual check-ups, prescription refills, or reminders to patient surveys.
Conclusion
Integrating Robotic Process Automation with EMR systems such as eClinicalWorks, ModMed, and SimplePractice is a practical step towards modernizing healthcare. The RPA automatically automates repetitive functions, reduces errors, and saves time, allowing employees to focus on patient care. While challenges such as setup costs and system maintenance exist, benefits—better efficiency, happy patients, and a healthy business—outweigh them.
By understanding its limits and planning carefully, clinics can use RPA to unlock the full potential of their EMR system. This technique is not about changing people, but is strengthening them to give better care. As healthcare continues to develop, RPA is a reliable tool to improve efficiency and increase patient experiences.








