Key Takeaways
- Voice AI succeeds when it blends into a technician’s workflow, not when it forces them to learn a new system or carry extra devices.
- Logging, escalation, and scheduling benefit most from voice enablement, delivering measurable improvements in speed, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
- High-noise environments, jargon, and poor escalation protocols can cripple AI performance—technical and process readiness are just as important as the technology itself.
- The real ROI isn’t just in saved minutes, but in better compliance, richer data for predictive maintenance, and stronger customer trust.
- Phased rollouts with technician involvement consistently outperform top-down deployments in adoption rates and long-term success.
If you’ve ever shadowed a field technician for a full day, you know the job isn’t just “fixing the thing.” It’s juggling diagnostics, customer updates, inventory checks, and compliance logs—all while balancing on a ladder or crouching under an HVAC unit. The irony? Many of the slowest and most frustrating parts of the work aren’t the technical repairs themselves, but the administrative tasks that bookend them.
Voice AI is starting to pull its weight here—not as a gimmick, but as a tool that seamlessly integrates into the technician’s day, just like a torque wrench or a multimeter. It’s not about “digital transformation” for the sake of it. It’s about shaving minutes (and mistakes) off every job in ways that compound over a week, a month, or a quarter.
This isn’t theory. Service organizations in utilities, telecom, and heavy equipment maintenance are already rolling out voice interfaces for three very specific, very painful workflows: logging, escalation, and scheduling.
Also read: From Live Chat to AI Chat: Automating Customer Conversations with Purpose
Logging Without Losing the Day
One of the great paradoxes in field service: the more complex and valuable the repair, the more paperwork it generates. Warranty claims, asset lifecycle tracking, and regulatory compliance—all require accurate logs. Yet these logs are often captured hours after the work is done, when the tech is back in the van or at home, trying to reconstruct the details from memory.
The consequences of that delay are predictable: missing serial numbers, vague fault descriptions, and skipped steps in the audit trail.
Voice AI’s role here is deceptively simple: enable the tech to “talk through” the log as they work, without breaking stride. The AI doesn’t just transcribe—it tags, timestamps, and matches entries to job IDs, parts catalogs, or compliance templates.
A utility company in the Midwest trialed this in their transformer maintenance teams. Instead of filling out 18-field forms back at the depot, technicians wore ruggedized headsets. After replacing a high-voltage bushing, they could say, “Log replacement of bushing on unit 4579, use part code HVB-22, cause of failure thermal fatigue, photos attached.”
The system automatically appended the location via GPS, pulled warranty status from the ERP, and even linked thermal imaging photos taken earlier. A process that once took 12–15 minutes per job dropped to under 90 seconds.
Where it shines:
- Real-time accuracy – Details are fresh; no guessing later.
- Hands-free operation – Critical when working at height or in confined spaces.
- Integration hooks—Entries flow directly into CMMS, ERP, or compliance databases.
Where it stumbles:
- High-noise environments—Without advanced noise cancellation, accuracy tanks.
- Specialized terminology—Industry jargon or local nicknames for parts can still trip up speech models unless trained with domain data.
The takeaway? Voice logging is not about replacing the human narrative—it’s about capturing it before it evaporates.
Escalation Without Losing the Customer
Escalations are the hidden iceberg of field service costs. On paper, they’re just “handoffs” to a senior technician or specialist. In practice, they often involve:
- Waiting on hold with a support desk.
- Searching for a contact in a directory buried three menu layers deep.
- Repeating fault descriptions multiple times.
By the time the right expert is looped in, the customer has been pacing the floor for 40 minutes, wondering if the tech on site knows what they’re doing.
Voice AI can strip that latency out of the process. The best implementations work like this:
- The tech describes the issue verbally.
- AI parses the context (equipment type, error codes, symptoms).
- It matches the problem to escalation protocols or specific experts.
- It initiates a live voice/video bridge—or opens a shared AR view—without the tech navigating a phone tree.
A real-world illustration:
A global elevator maintenance firm equipped its teams with AI-powered comms headsets. When a junior tech hit an unexpected hydraulic fault, they said, “Escalate: Hydraulic pump model HPL-900, error code 62, abnormal pressure reading.”
The AI identified the fault as rare but documented, matched it to an internal knowledge base entry, and connected the tech directly to one of the two engineers certified on that subsystem. Total time from detection to expert on the line? Three minutes. Previously, it averaged 25.
Nuances worth noting:
- AI-assisted escalation isn’t magic—it’s as strong as the organization’s contact maps and fault taxonomy.
- Poorly maintained escalation trees will bottleneck the AI as much as they do humans.
- Privacy and security aren’t trivial. Escalation calls can inadvertently expose sensitive site data; compliance frameworks need to keep up.
In other words, Voice AI is a speed multiplier, not a substitute for having the right escalation playbooks in place.
Scheduling Without the Spreadsheet Headache
Scheduling is where optimism meets reality in field operations. The central team may build a neat roster of daily visits, but real-world conditions—traffic, missing parts, overlong repairs—blow it up by lunch.
Technicians in the field often have to renegotiate their day on the fly. Without AI, that usually means calling dispatch, waiting for them to reshuffle the list, and hoping nothing critical gets dropped.
With voice-enabled scheduling, a tech can say, “Push next appointment by 45 minutes; traffic delay on I-95. Reassign the site visit to Tech 12 if available.”
The AI checks technician availability, location, skill fit, and even service-level agreement (SLA) priorities, then proposes adjustments for approval. Some systems can auto-confirm with the customer via SMS or app push.
One facilities management company rolled this out across 220 mobile teams. They reported:
- Reduced dispatcher call volume by 40%.
- Same-day job completion rate improved by 12%.
- Technician satisfaction scores (yes, they measure them) went up because they no longer felt micromanaged—they were collaborating with the schedule, not being dictated to by it.
The Integration Puzzle
All three of these workflows—logging, escalation, and scheduling—only work seamlessly if the Voice AI is integrated into the systems technicians already use. This is the crux.
A voice interface that requires switching devices, duplicate data entry, or learning an alien set of commands will die in the field. The tech adoption rate will be brutal.
In my experience, the deployments that succeed share a few traits:
- Embedded in existing devices – Tablets, rugged smartphones, or comms headsets already in the kit.
- Context-aware commands—”Log “replacement” means different things in HVAC vs. telecom; the AI needs to know the domain.
- Offline tolerance—Fieldwork often happens in coverage dead zones. Local processing with deferred sync is a must.
When Voice AI Overpromises
Vendors will often claim their solution “works anywhere, with any workflow, out of the box.” In reality:
- Accent and dialect handling still vary widely.
- Cross-language support is immature when mixing technical English with local languages.
- User training is non-negotiable. Technicians won’t magically use the right phrasing; they need onboarding and periodic refreshers.
And yes, some technicians just won’t use it—ever. There’s always a percentage of the workforce that resists new tools, and field service has a strong “if it ain’t broke” culture. That’s not necessarily bad; it forces project teams to prove value before scaling.
The Business Case—Beyond the Obvious
It’s tempting to frame Voice AI purely in terms of time saved, but the ripple effects are bigger:
- Customer trust—Faster escalations and proactive scheduling updates reduce friction.
- Compliance—Accurate logs protect the company in warranty disputes or safety investigations.
- Training—Recorded voice logs become real-world case material for onboarding new hires.
- Data quality—Voice capture, done right, enriches asset histories, making predictive maintenance models more reliable.
Interestingly, some firms have found that the unexpected benefit is in cross-department collaboration. Maintenance logs spoken on-site get transcribed and made searchable; engineering can spot recurring design flaws without waiting for quarterly review meetings.
A Practical Rollout Blueprint
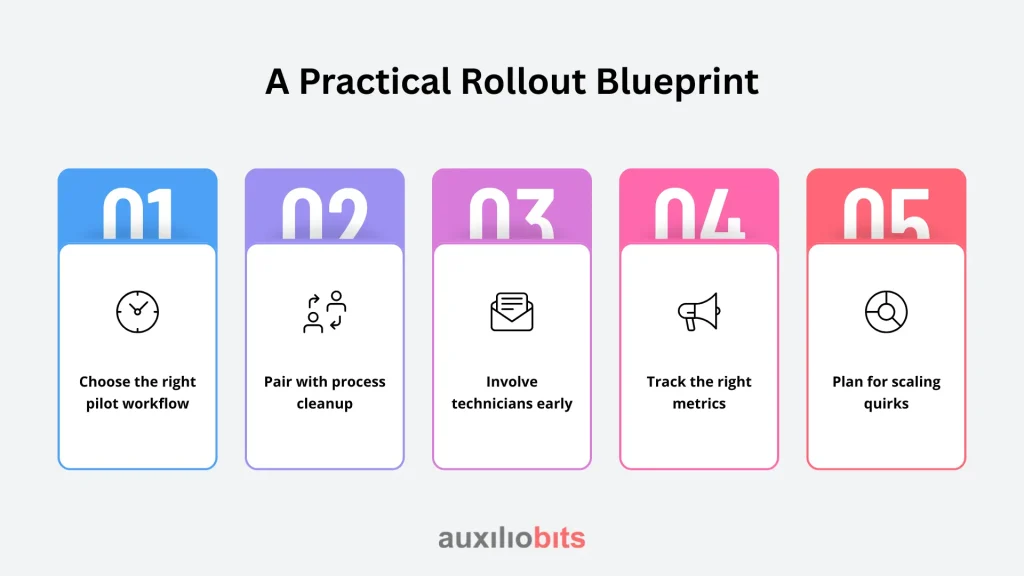
1. Choose the right pilot workflow
Logging is often the lowest-hanging fruit—it’s structured enough for automation but flexible enough to show quick wins.
2. Pair with process cleanup
Don’t automate broken workflows. If your escalation contacts are outdated, AI won’t fix that.
3. Involve technicians early
They’ll tell you the edge cases you didn’t think of—like “What happens when I’m 30 feet up and the headset battery dies?”
4. Track the right metrics
Not just time saved—also error reduction, customer satisfaction, and first-time fix rate.
5. Plan for scaling quirks
AI models need retraining as they encounter new jargon, accents, and failure modes. Treat them like apprentices—they learn on the job.
The Final Thoughts
Voice AI in field service is not about “replacing” technicians or wrapping everything in some futuristic veneer. It’s about making sure the skilled human on-site can focus on what they do best—diagnosing, repairing, and ensuring the customer’s problem is solved—without being buried under the admin work that too often defines their day.
Done well, it becomes invisible: the tech speaks, the systems update, the schedule flexes, and the right people are looped in. No drama. No duplicated effort. And that’s the point.








