Key Takeaways
- Logistics pricing has outgrown rule-based systems. Agentic AI handles real-time complexity, trade-offs, and permutations that human teams and static rules cannot scale.
- Agentic AI acts, not just advises. Unlike traditional AI, agents autonomously adjust prices within guardrails, learning continuously from market outcomes and feedback loops.
- Dynamic repricing is contextual, not reactive. Effective agentic pricing balances margin, service quality, contracts, and client relationships—shipment by shipment.
- Learning loops drive sustained advantage. Reinforcement signals, simulations, and historical trends allow agents to refine pricing strategies over time, not just respond to events.
- Governance determines success. Transparent reasoning, risk controls, and human oversight are essential to prevent over-automation and maintain trust in autonomous pricing decisions.
Pricing in logistics has always been more art than science. Shippers, carriers, and brokers wrestle with fluctuating fuel costs, seasonal demand swings, last-minute capacity crunches, and client-specific contract nuances. Historically, teams have relied on spreadsheets, historical benchmarks, and intuition. It worked… mostly. But in a market where margins are razor-thin, small miscalculations ripple into lost revenue, stranded inventory, or angry clients. Enter Agentic AI—a new breed of autonomous systems that don’t just crunch numbers; they perceive, decide, and act across complex pricing landscapes.
The Challenge of Logistics Pricing Today
Consider a mid-sized freight broker managing hundreds of shipments daily. Each route has multiple constraints:
- Carrier availability and reliability
- Client urgency and volume commitments
- Real-time fuel and toll costs
- Regulatory compliance per region
- Competitor rates that shift by the hour
Now, imagine manually updating quotes for each client. Even with pricing software, most systems operate on rules: “If the fuel surcharge rises 5%, adjust the rate by 2%.” These rigid rules don’t capture nuanced trade-offs, like balancing profitability with client retention or adjusting prices in anticipation of demand spikes.
A human pricing analyst can make judgement calls, sure, but only for a fraction of the possible permutations. And as volume grows, delays, missed opportunities, or overcompensation creep in. That’s where agentic AI proves its value—not as a replacement for human judgement, but as a partner capable of real-time, scalable decision-making.
What Makes Agentic AI Different?
Agentic AI differs from traditional automation or even conventional AI in a subtle but critical way: it acts autonomously within defined boundaries, continuously learning from outcomes. Traditional AI or RPA might recommend price adjustments based on historical trends. Agentic AI, on the other hand, can:
- Observe market shifts in real time, including competitor behavior.
- Evaluate multiple pricing strategies simultaneously and select the optimal path.
- Adjust individual shipment or contract rates dynamically without waiting for manual approval.
- Learn from feedback loops, like lost bids, client pushback, or carrier cancellations, to refine future decisions.
In short, these agents can operate almost like junior pricing strategists, constantly scanning the market and internal systems, weighing trade-offs, and executing adjustments across hundreds or thousands of pricing scenarios in minutes.
Also read: Why Agentic AI Will Accelerate the Age of Outcome-Based Work
Dynamic Repricing in Practice
Dynamic pricing in logistics is not about raising rates arbitrarily—it’s about contextual sensitivity. Some examples illustrate why agentic AI is uniquely suited:
1. Last-Mile Surge Management
Retailers during holiday seasons often experience sudden last-mile demand spikes. Human teams struggle to recalibrate rates across multiple carriers. An agentic AI can monitor real-time delivery loads, evaluate carrier reliability, and adjust surcharges to optimize both margin and service quality—all within seconds
2. Spot Market Adjustments
Spot freight rates fluctuate based on available capacity. Agents can continuously scrape carrier spot rates, predict likely trajectories, and automatically generate competitive bids. For instance, if the agent detects a 10% drop in regional spot rates, it can reprioritize shipments to the most cost-effective carriers, avoiding unnecessary spend.
3. Contract-Sensitive Repricing
Large shippers operate under multi-year contracts with variable clauses—volume discounts, early payment incentives, or fuel-adjustment formulas. Agentic AI can factor in these clauses, calculate net profitability under multiple scenarios, and propose adjustments without breaching contract terms—a task far too intricate for manual calculation at scale
How Agentic AI Learns and Adapts
Learning logistics pricing is more complex than in traditional e-commerce. Agents must account for:
- Historical pricing and win/loss data
- Carrier performance variability
- Regional regulatory shifts
- Macroeconomic factors like fuel or port congestion
- Customer elasticity and loyalty
A single feedback loop isn’t enough. Agentic AI typically uses multi-tiered learning architectures:
- Reinforcement signals for immediate outcomes (e.g., bid acceptance or rejection)
- Trend-based adjustments from historical data
- Predictive simulations to anticipate market changes hours or days ahead
It’s fascinating to see how agents refine their strategies over time. For instance, an agent may initially overestimate price elasticity in a new region, losing a few bids. But within weeks, the system recalibrates, balancing competitiveness with profitability. Humans rarely notice these micro-adjustments, but they cumulatively enhance bottom-line performance.
Key Benefits
Organizations that integrate agentic AI for pricing and repricing often report the following benefits:
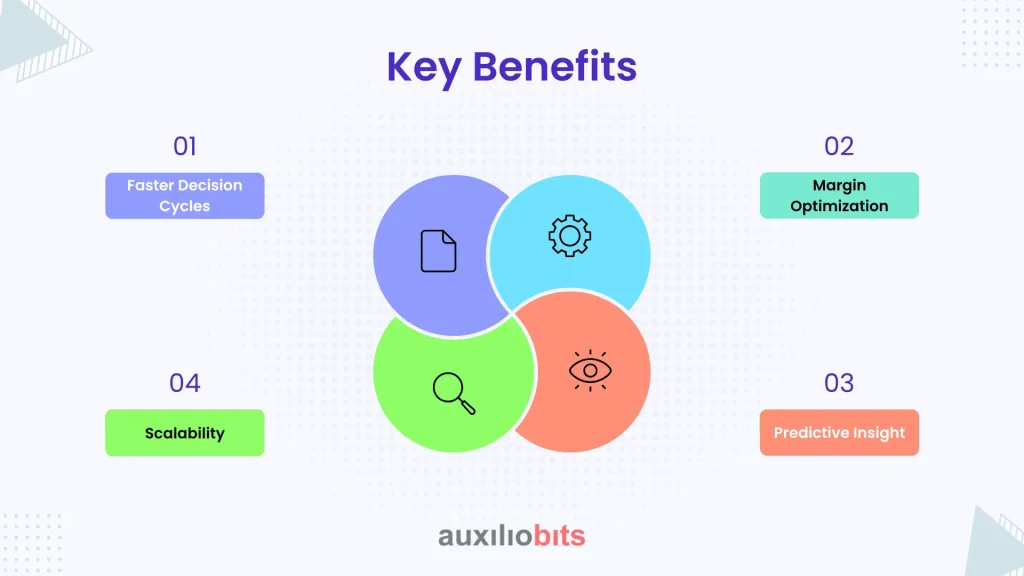
- Faster Decision Cycles: Seconds instead of hours, allowing dynamic adjustments across thousands of shipments.
- Margin Optimization: Consistently captures optimal rates while reducing human error.
- Scalability: Agents can simultaneously manage multiple clients, carriers, and contracts.
- Predictive Insight: Beyond reactive pricing, agents anticipate market shifts and recommend preemptive adjustments.
But benefits are nuanced. Over-automation without oversight can backfire. Agents might push rates too aggressively, triggering client dissatisfaction. Achieving a balance between autonomy and guardrails is crucial.
Implementation Considerations
Before jumping in, logistics firms must think beyond the technology. Several factors affect success:
1. Data Quality and Accessibility
Agents rely on accurate, timely data. Legacy TMS or ERP systems often have inconsistent input formats. Cleaning and structuring this data is foundational.
2. Integration Across Systems
Pricing doesn’t exist in isolation. Agents must interface with CRM systems, shipment tracking platforms, and carrier portals. Fragmented integration can create blind spots.
3. Risk Management Policies
Autonomous pricing decisions must respect contractual obligations, regulatory limits, and internal thresholds. Define guardrails explicitly.
4. Explainability
Even autonomous agents should offer reasoning trails: why a rate changed, which carriers were prioritized, or what market signals influenced decisions. Without transparency, human teams resist adoption.
5. Continuous Monitoring
Deploying an agent isn’t “set it and forget it”. Regular audits ensure it learns correctly and remains aligned with strategic goals.
Agentic AI for dynamic pricing in logistics isn’t magic. It’s a disciplined blend of autonomous action, learning, and market awareness, applied in a domain where speed, accuracy, and nuance matter. It thrives where humans are overwhelmed by permutations, yet falters without structured oversight.
For logistics leaders, the real question isn’t whether to experiment with agentic AI—it’s how to integrate it responsibly, with clear data pipelines, guardrails, and human-in-the-loop checkpoints. Done right, the technology doesn’t just automate pricing; it redefines how decisions are made, in real time, across complex, interdependent systems.