As your organization takes the Automation initiatives it becomes imperative to work hard on building an efficient Center of Excellence (CoE) whose members comprise of various roles needed for RPA implementation. The Automation First thinking is indispensable in today’s fast changing business scenario but comes with challenges that need to be overcome.
One of the major roles in the RPA Center of Excellence is that of the RPA Solution Architect. Various businesses have different approaches in embarking the automation journey. Some prefer building the CoE in-house and some prefer to hire experts for their proven professional services. But the role of the RPA Solution Architect remains very demanding and can shape the future of the automation journey being undertaken. To understand the role of the RPA Solution Architect the following are discussed in a nutshell to have a better understanding of where the architect fits in the whole RPA journey:
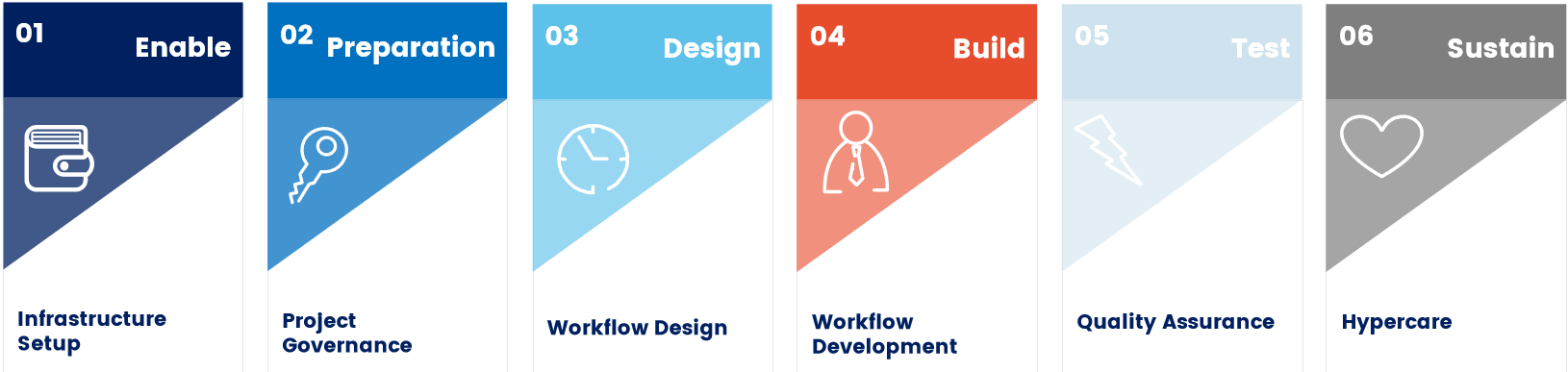
RPA Project Stages
An automation initiative and journey involves various stages for each of the RPA projects being undertaken. Some of the major stages of an RPA project are:
- Infrastructure Setup: This includes designing the server architecture, Installing and configuring the architecture and setting up development, test and production environments for the RPA to run.
- Project Governance: This involves agreeing on the project development approach and reviewing the RPA best practices.
- Workflow Design: Filling in the Process Design Document (PDD) is where various processes to be automated are defined. Various test cases and data and designing the solution is involved in this process.
- Workflow Development: This stage includes developing the workflows according to the PDD, performing unit and functional testing and once done create the Development Specification Document (DSD).
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring quality is achieved through executing the test cases and reporting the results and as a result making the decision to continue with the deployment or revisit the workflows.
- Hypercare: Performing workflow support and managing changes and improvements are performed in this stage.
Background and Skillset of an RPA Solution Architect
An RPA Solution Architect should be a seasoned software professional with more than 5 years of programming experience in any one of the popular programming languages like for .NET (C#, C++ or VB) and/or Java. A solution architect should have a lot of experience working in the service industry and a similar business setup to understand the business processes and the technical architecture of the solutions.
Infrastructure knowledge including servers, storage, firewalls, load balancers, routers etc. is imperative in getting things rolling. An RPA solution architect is no ordinary developer and should have strong conceptual and analytical skills and should be result oriented. Most importantly a solution architect should be able to develop solution architect designs. A good RPA solution architect is a team player with leadership and cross-team collaboration experience.
Responsibilities and Ownership of the RPA Solution Architect
A solution architect is the pillar of an organization’s RPA implementation and has to perform various responsibilities to make sure the solution when deployed will serve the purpose of automation with no glitches. Most of the responsibilities include:
- Enabling the RPA solution to be developed and deployed: The solution architect is responsible to oversee the initial infrastructure setup for the dev, test and production environments. The solution architect also explores the server and other RPA deployment options.
- Preparing for the RPA journey: The solution architect is responsible for getting everyone on the CoE including the stakeholders to agree on the best practices to be followed. She makes sure that proper coding standards and guidelines are laid out. Collaborating with the Business Analyst on feasibility and optimization is undertaken. As part of the preparation the solution architect is also responsible to estimate the time and cost and plans on the technical meetings to be conducted during the process.
- Designing the solution: Once the Process Design Document (PDD) is signed off, the overall solution is designed and documented. This includes the component splitting and appointing developers to develop each component and/or workflow. The solution architect is responsible for identifying reusable components that can save duplicate effort and also defining how to manage configurable parameters, queues and schedules of Robots to optimize the cost and runtime. A document describing outstanding challenges is also created to log any challenges that may or may not be taken care of during the implementation.
- Building the workflows: The solution architect oversees the development effort being carried out to develop the component workflows and is responsible to document extra requirements after the PDD has been signed-off. A good RPA solution architect mentors the developers through constant monitoring and helps in troubleshooting and debugging of the issues. She is the source control owner and makes sure the logging and reporting happens as per the requirements laid down.
- Testing: An impeccable solution design and implementation needs testing at various levels of the design and implementation. A timely and diligent code review and audit by a solution architect ensures there are fewer bugs and the solution is compliant and robust. A Development Specification Document (DSD) is reviewed and signed-off and the functional testing is performed to be able to pass the acceptance testing.
- Sustaining the solution: As part of the Monitoring and Control the solution developed and deployed is monitored and any changes needed are documented in addition to the support provided to fix any unknown issues popping out of the production environment.

An RPA Solution Architect for your RPA journey
An RPA solution architect serves as a pillar in the RPA journey and for the RPA Center of Excellence that is involved in automating various processes in an organization. She provides constant monitoring, mentoring of the RPA developers and continuously increases the capabilities of the RPA developers. An architect lays down the guidelines for logging and reporting and helps in troubleshooting and debugging of the issues popping out. As she is the source control owner of the solution, an architect is responsible for performance improvements and quality checks from time to time. Managing risk mitigation and identifying risks is an integral part of the solution architects job. If you are to look upon somebody to solve complex technical issues then the RPA solution architect is the go-to person.
Most organizations try to train a person in-house for architect role but still getting an expert on-board can save time and bring in professional experience onto the CoE panel.
For training a solution architect inhouse or getting an experienced RPA solution architect onboard please get in touch with us now!




 April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024
